I was in Detroit a few weeks ago for the RE-AMP Annual Meeting. I was there for reasons that were largely ancillary to the meeting itself. I’m not a member of the RE-AMP network. I wasn’t giving a talk. I didn’t participate in the design or facilitation, other than offering a thought or two when asked.
Still, my experience there felt like validation for everything I’ve been working on over the past two years. It was an incredible high, and it also demonstrated how much work still remains to achieve my larger goal of wide-scale collaborative literacy.
Success Breeds New Challenges
RE-AMP is a network of over 160 organizational members focused on climate change in the Midwest. Their shared goal is to reduce regional global warming emissions 80% by 2050.
It was co-initiated over a decade ago by my friend and former colleague, Rick Reed, who had a simple question he wanted to test:
What would happen if nonprofits and foundations alike took the time to sit down together to really, truly, deeply understand the system they were all trying to change?
So he tested it. With the backing of the Garfield Foundation, he brought together a small group of leaders in the Midwest working on climate change and convinced them to sit together, listen to each other, and strategize together.
The process took almost two years. It was messy and expensive, and it teetered on total and utter failure on multiple occasions. But it worked. Participants arrived at a shared epiphany about what the critical levers were for stopping climate change. The trust and relationships that were built and strengthened through the process led to quick and aligned action among nonprofits and foundations alike around those leverage points.
This strategic alignment resulted in many immediate wins, the most eye-opening being stopping 30 coal plants in the Midwest.
Success created new problems. The hard work of thinking and planning together had forged a collective attitude, a network mindset among the initial participants that drove the way they worked. Their success attracted new participants very quickly, but the shared understanding, the relationships, and the network mindset did not scale at the same pace.
Over the past few years, the network has made a number of moves to try to shift this. Most notably, they hired a network CEO and additional full-time “staff” members to be able to respond more quickly to the needs of the network. (RE-AMP is not its own legal entity. Its “staff” are all employed by other organizations distributed throughout the network.)
This investment in internal capacity has enabled the network to start addressing structural and bigger picture issues that had previously been left by the wayside. One of those issues has been re-integrating systems thinking and a more collaborative mindset back into the DNA of the network.
Helping Groups Help Themselves
Three years ago, I left the consulting firm I co-founded and a team that I loved in order to seek greater balance and impact. I felt that I was doing some of the best work in the field, but it was not translating into the larger-scale impact I was hoping for.
Ever since I got into this business in the early 2000s, I’ve always explained my vision of the world and theory of change with a simple thought exercise:
Think about the best collaborative experience you’ve ever had.
What would your life be like if all of your collaborative experiences were as good as that one?
What would the world be like if everyone’s collaborative experiences were all that good?
How about if everyone’s collaborative experiences were all just slightly better?
I believed (and still believe) that the world would be significantly better if we saw incremental improvement in people’s collaborative literacy across the board at scale.
However, that’s not where I focused my energy. I liked working on hugely complex problems that required cutting-edge capabilities. I did the work inclusively — the only way you had a chance to solve these kinds of problems — with the hope that people would learn enough through the experience that they could continue working in a similar way. Furthermore, I hoped that by openly sharing what I learned, I could have a broader impact than just the projects I was working on.
Both of these turned out to be true, but not appreciably so. The way I was working was benefiting me more than anyone else. It was an incredible opportunity for me to practice and learn and to do work that was joyful and meaningful, and it helped me establish a reputation that created more opportunities. Others were also learning from these experiences, but they weren’t as invested as I was, and there were few structural incentives for them to continue developing their skills after we finished the project.
If I wanted to stay true to my vision, I needed to focus on sustainable interventions for helping others develop their collaborative capabilities. I do not believe that the ability to collaborate effectively is some mystical talent with which only a select few are imbued. I believe that everyone has the ability to be much, much better. All people need are opportunities to practice.
For the past two years, I’ve been focused on creating those opportunities. I’ve been testing workouts and tools designed to help people develop stronger collaborative muscles and mindsets. I stopped doing work for groups and have focused instead on helping them develop the skills to help themselves. I’ve also been mentoring emerging practitioners who want to go the extra mile in developing their skills.
The Meeting
In some ways, RE-AMP has been an ideal testbed for my workouts and tools. Because it’s a decentralized network, it can’t change culture or practices by fiat (or by firing) the way an organization can. Practices have to work, otherwise they will be ignored, and they have to be adopted widely, otherwise they will be rendered ineffective.
Furthermore, its history of great work, strong relationships, and growing internal capacity served as a strong foundation. Its staff, along with many of the informal leaders in the network, are bold, talented, and hungry to learn.
I ran an early pilot of my Collaboration Muscles & Mindsets program with the RE-AMP staff last year. It went okay. Some things were well-received, some not so much. I developed an assessment to help me determine whether or not my program was working, but the main thing I learned was that my assessment needed improving.
Still, the program was effective enough that they were interested in making it available to the broader network. For the past few months, we’ve been discussing and planning a program that will launch early next month.
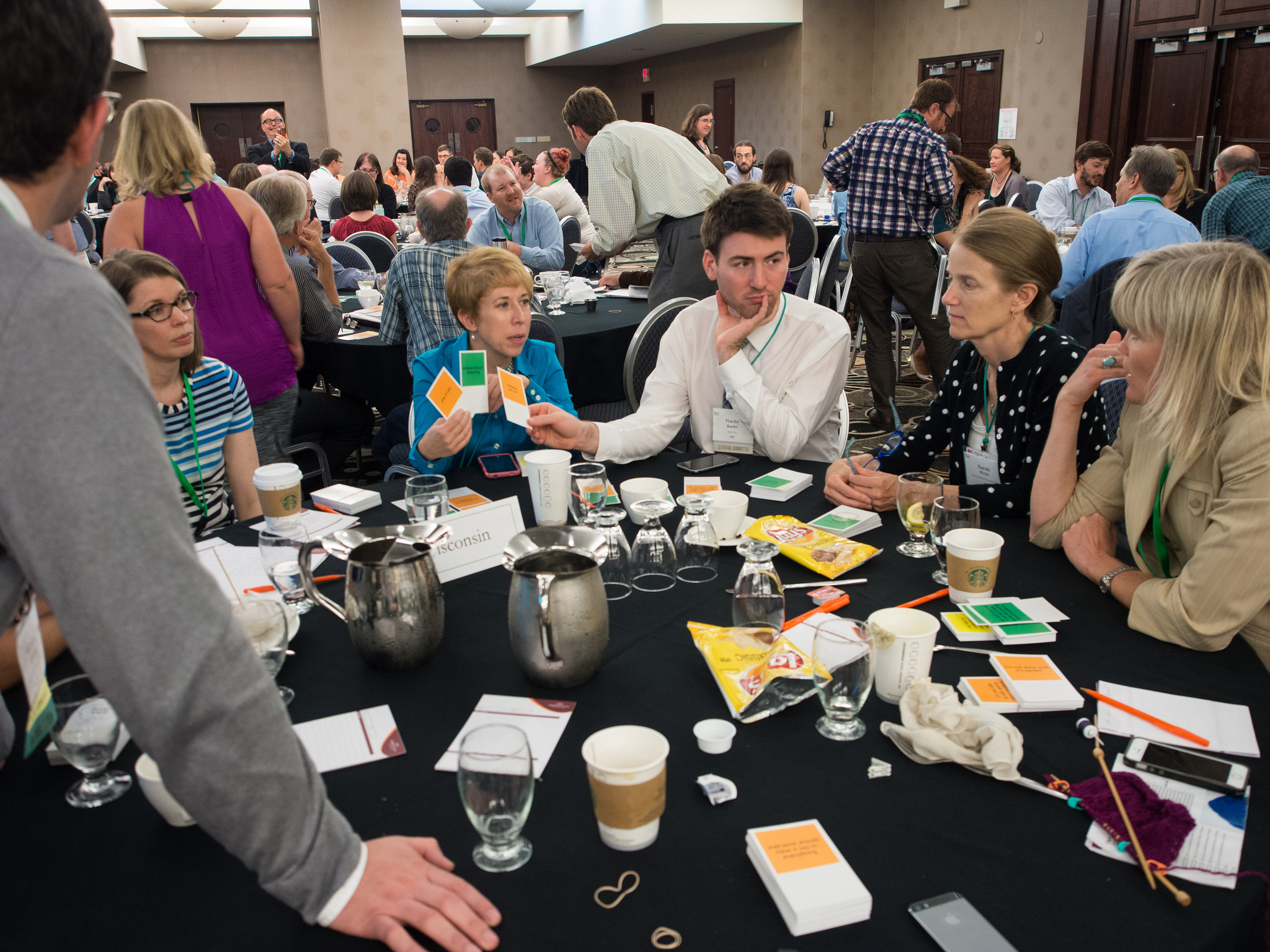
In the meantime, unbeknownst to me, the RE-AMP staff was cooking up something interesting on their own. They had decided to run a session at their Annual Meeting based on a Muscles & Mindsets exercise I had led them through at their staff meeting for a dozen people the previous year. They were going to adapt it for 160.
Scaling up the exercise would actually be relatively straightforward. Most exercises I design are meant to scale. Understanding this conceptually, though, and believing it enough to do it in a real-life, high-stakes situation takes courage, especially if you haven’t done it before. This is one reason why people hire people like me to do this for them.
But the RE-AMPers weren’t going to bother with that. They had the audacity to try it on their own. Prior to the meeting, they walked me through what they were going to do, and I made some suggestions and offered encouragement. Beyond that, I had nothing to do with the session.
Watching the session was exciting on many levels. First, Sarah Shanahan and Trevor Drake expertly facilitated the exercise. They had a calm energy, and they gave clear instructions with compelling, relevant examples. They managed to command a large, rowdy room of people by giving up control, which the participants appreciated and which one person made a point of noting during the debrief.
Second, it was a thrill to watch 160 people using a toolkit — our mindset cards — that I had invested a few years and a ton of energy into codesigning. At my previous consulting firm, I had done a lot of organizational culture work with my friend and business partner, Kristin Cobble, who had introduced me to a framework for mapping mindsets to behaviors. It was effective, but also high overhead, and it required facilitators who were very literate with the framework. For example, it took us four months to do this work with a 75-person organization, and that was an accelerated process!
My motivation for designing the cards was to see if we could create a tool that would allow groups to condense a multi-month conversation into a few hours and to allow them to have that conversation without the aid of a framework expert. There were several examples of groups using the cards to great success with groups of 10-15, and I was confident that larger groups could benefit from them as well. But I hadn’t seen it… until the RE-AMP meeting.
It was amazing to watch 160 deeply engaged in conversation using the cards, and it felt even better knowing that they were able to do it without my help. I walked around the room, eavesdropping on conversation, peeking at people’s cards, and soaking in the buzz. I was in heaven.
Third, I was surprised by what happened. Gail Francis, who led the design of this session, had made a decision about something relatively minor against which I had advised. The final exercise for the 20 groups of eight was to use the cards to agree on a set of mindset “spectrums.” The question was how to capture these. I had suggested that the groups write them on a worksheet, then bring them to her. She decided to have people hold up their cards, which she would then collect and transcribe for them. It was a tradeoff between saving time for the participants and saving time for the facilitators.
She understood the trade-off and chose saving the participants’ time. That led to something completely unexpected — groups cheering in excitement every time they completed the exercise. It was fun, it was funny, it bolstered the already high energy in the room, and it likely wouldn’t have happened had she chose what I had suggested.
We’re Not There Yet
I’ve devoted the last two years to developing methods and tools that help groups help themselves. Seeing this work manifest itself this way at the RE-AMP Annual Meeting was gratifying and validating. Every group already has smart, capable people who have the potential to unleash the group’s intelligence. All they need is space, a little guidance, and room to practice and learn.
For this meeting, a few people got that space, and the results were outstanding. They were also only a fraction of what’s possible. As good as they were, they could have been much, much better. They’ll get there if the people in the network are given that room to practice their skills in bigger and more ambitious ways. Unfortunately, most groups do not give people that space.
All too often, “experimenting” consists of one-offs. Mastery doesn’t happen in a one-off. It takes time and commitment and lots of stumbling. In order to raise the bar and create the space for that growth, people need to experience what’s possible. Most people have such poor collaborative experiences, they either flinch and give up at the first sign of trouble, or they stop taking risks after they experience a small win. RE-AMP is ahead of most groups in this regard, but still, I wonder.
If my workouts and tools are going to have a chance at making an impact, then I need to find ways to make it safe for people to commit to them, and I also have to give people the experience of what’s possible. I’m currently exploring ways to do exactly that. In the meantime, I’m appreciating what I’ve accomplished so far and the people who have taken me there, and I’m excited about what’s coming next.
Thanks to Greg Gentschev and H. Jessica Kim for reviewing early drafts of this post.
Correction: The originally published version of this post stated that this was the first time the RE-AMP staff had decided to design and facilitate their Annual Meeting on their own without external facilitation. Gail Francis pointed out that this was not correct. While their early meetings had been designed and facilitated externally, they had actually been designing and facilitating their meetings on their own for several years. I removed my incorrect claim in this version.